What Device Does This Mac Address Belong to
How would you communicate with a device when you don't have the IP?
You might exist in a situation where you don't take the IP address of a device in a local network, but all you take is records of the MAC or hardware accost.
Or your computer is unable to brandish its IP due to various reasons, and you are getting a "No Valid IP Address" mistake.
Finding the IP from a known MAC address should be the task of a ReverseARP application, the counterpart of ARP. Merely RARP is an obsolete protocol with many disadvantages, so information technology was apace replaced by other protocols like BOOTP and DHCP, which deal directly with IP addresses.
In this commodity, nosotros'll show yous how to notice all ip addresses on a network along with device vendors using MAC addresses with different methods for gratuitous.

Related mail service: How to Scan network for IP Addresses
Understanding ARP
ARP (Accost Resolution Protocol) is the protocol in charge of finding MAC addresses with IPs in local network segments.
It operates with frames on the data link layer. As you might already know, devices in the data link layer depend on MAC addresses for their advice. Their frames encapsulate packets that contain IP address information.
A device must know the destination MAC address to communicate locally through media types like Ethernet or Wifi, in layer 2 of the OSI model. Understanding how ARP works can help you detect IPs and MAC addresses quickly.
The following message menstruation diagram tin help you understand the concept:
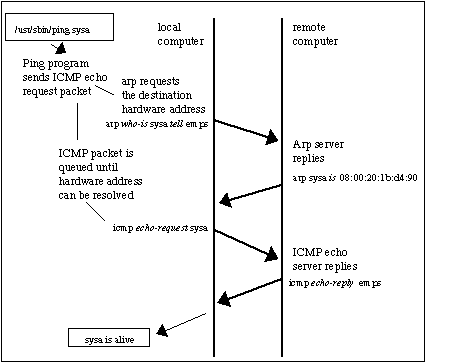
- The local computer sends a ping (ICMP repeat request) to a destination IP accost (remote computer) inside the same segment. Unfortunately, the local computer does not know the MAC accost… information technology only knows the IP address.
- The destination hardware address is unknown, so the ICMP echo request is put on hold. The local computer only knows its source/destination IP and its source MAC addresses. ARP uses two types of messages, ARP Request and Reply.
The local computer sends an ARP Request message to find the owner of the IP address in question.
This bulletin is sent to all devices inside the aforementioned segment or LAN through a circulate MAC (FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF) as the destination.
- Because the remote computer is role of the aforementioned network segment, it receives the circulate bulletin sent by the local computer. All other computers in the LAN besides receive the broadcast just they know that the destination IP is not theirs, so they discard the packet. Only the remote estimator with destination IP, responds to the ARP Asking with an ARP Answer, which contains the target MAC address.
- The local computer receives the ARP Reply with the MAC address. It then resumes the ICMP echo request, and finally, the remote computer responds with an ICMP echo reply.
Finding IPs with ARP
You can apply ARP to obtain an IP from a known MAC accost.
But first, it is important to update your local ARP table in club to get information from all devices in the network.
- Transport a ping (ICMP echo reply) to the entire LAN, to get all the MAC entries on the table.
- To ping the entire LAN, you can transport a broadcast to your network.
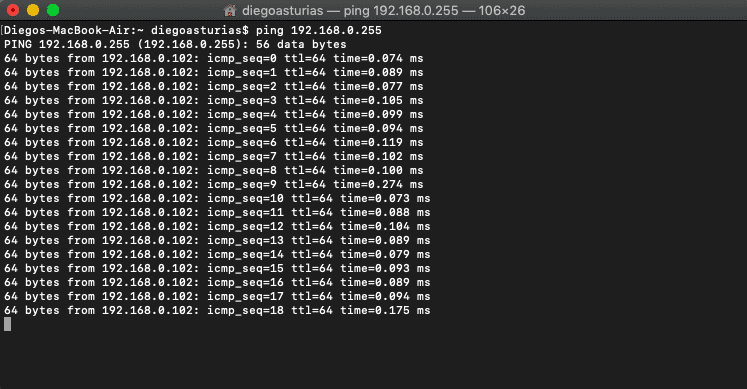
- Open the Control Prompt in Windows or terminal in macOS and type.
ping 192.168.0.255
My subnet is 192.168.0.0/24 (mask of 255.255.255.0), then the broadcast accost is 192.168.0.255 which can be calculated or establish with a "Print Route" control in Windows or a "netstat -nr" in macOS. Or tin can likewise exist obtained with a subnet figurer that you tin download for gratuitous.
For Windows:
Step 1
- Open the CMD (Command Prompt)
- Go to the "Start" menu and select "Run" or press [Windows-key] + [R] to open the Run awarding
- In the "Open" textbox blazon "cmd" and printing "OK".
This will open the control-line interface in Windows.
Pace 2
- Enter the "arp" command.
- The arp command without any boosted arguments will give you a listing of options that you can employ.
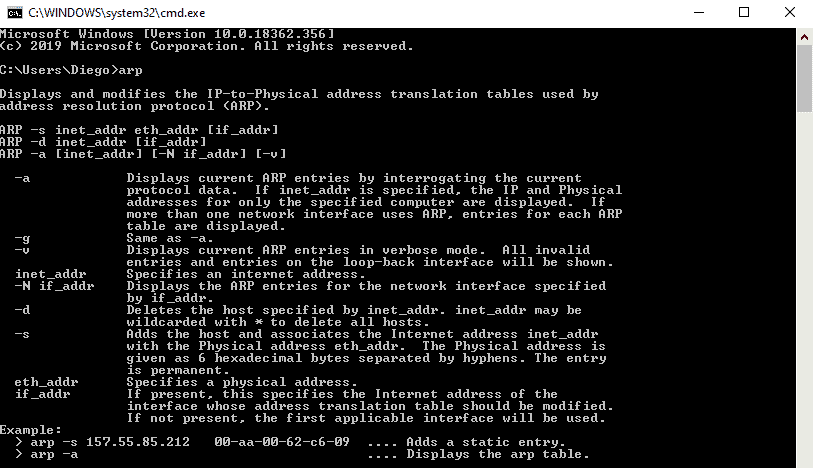
Step 3
- Use the arp with additional arguments to find the IP within the aforementioned network segment.
- With the command "arp -a" you can see the ARP table and its entries recently populated past your computer with the broadcast ping.
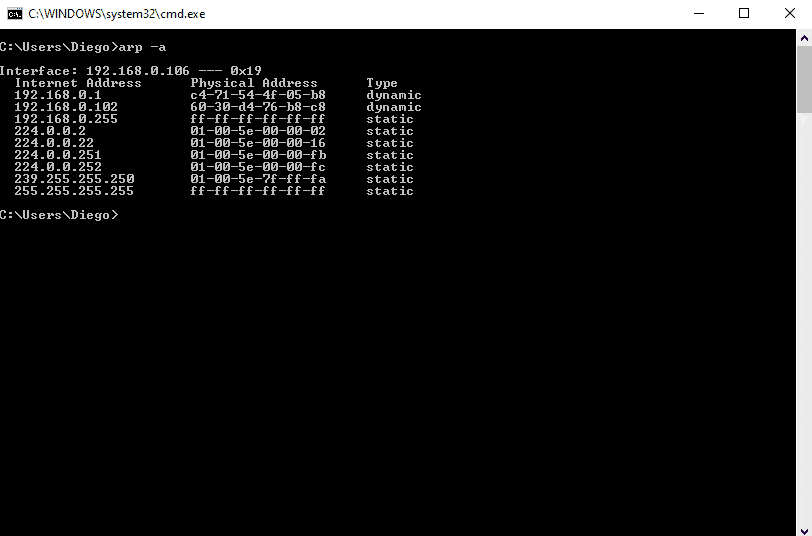
Stride 4.
- Reading the output.
- The information displayed in the arp-a is basically the ARP tabular array on your computer.
- It shows a list with IP addresses, their respective physical address (or MAC), and the type of allocation (dynamic or static).
Let'due south say you have the MAC address 60-xxx-d4-76-b8-c8 (which is a macOS device) and you lot desire to know the IP.
From the results shown in a higher place, y'all can map the MAC address to the IP address in the same line.
The IP Address is 192.168.0.102 (which is in the same network segment) belongs to 60-30-d4-76-b8-c8.
You can forget well-nigh those 224.0.0.x and 239.0.0.x addresses, as they are multicast IPs.
For macOS:
Stride 1
- Open the Concluding App. go to Applications > Utilities > Terminal or Launchpad > Other > Last.
Step 2
- Enter the "arp" command with an "-a" flag.
- In one case you enter the command "arp -a" y'all'll receive a list with all ARP entries to the ARP Table in your computer.
- The output will show a line with the IP address followed past the MAC accost, the interface, and the allocation type (dynamic/static).

Finding IPs with the DHCP Server
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is the network protocol used by TCP/IP to dynamically allocate IP addresses and other characteristics to devices in a network. The DHCP works with a client/server mode.
The DHCP server is the device in charge of assigning IP addresses in a network, and the client is usually your calculator.
For dwelling house networks or LANs, the DHCP Server is typically a router or gateway.
If y'all take access to the DHCP Server, you can view all relationships with IPs, MACs, interfaces, proper name of the device, and lease time in your LAN.
Step i
- Log into the DHCP Server. In this example, the DHCP server is the habitation gateway.
- If you don't know the IP address of your DHCP Server/ Gateway, you lot tin can run an ipconfig (in Windows) or ifconfig (in macOS/Linux)
- This particular DHCP Server/Gateway has a web interface.
Stride 2
- Enter the IP address on the search bar of the spider web browser, and input the right credentials.
Step 3
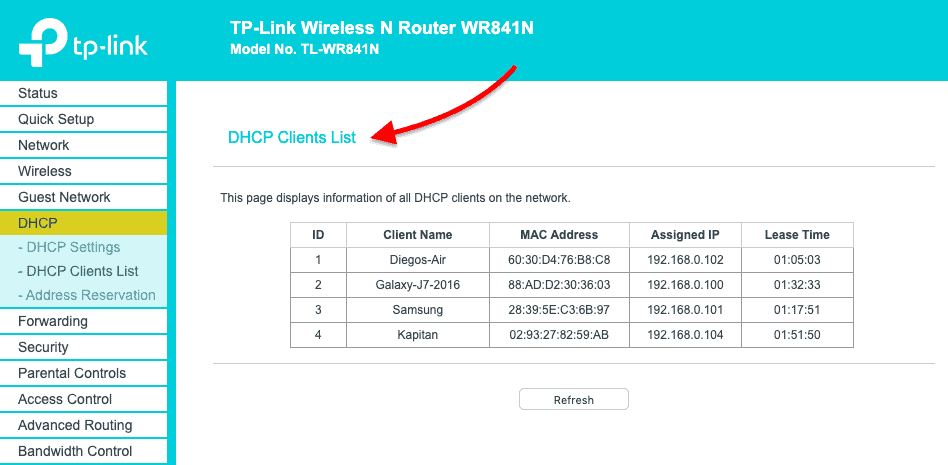
- Find the DHCP Clients Listing.
- In this TP-Link router, the DHCP Server functionality comes as an additional feature.
- Go to DHCP > DHCP Clients List. From this listing, you lot can see the mapping between MAC addresses and their assigned IPs.
Using Sniffers – Nmap
If you lot couldn't find the IP in the ARP list or unfortunately don't take access to the DHCP Server, as a last resort, you lot can apply a sniffer.
Bundle sniffers or network analyzers like Nmap (or Zenmap which is the GUI version) are designed for network security.
They can help identify attacks and vulnerabilities in the network.
With Nmap, you can actively scan your entire network and find IPs, ports, protocols, MACs, etc.
If you are trying to find the IP from a known MAC with a sniffer like Nmap, expect for the MAC address within the browse results.
How to find the Device and IP with a Sniffer?
Step 1
- Keep records of your network IP address information.
- In this example, my network IP is 192.168.0.0/24. If you don't know it, a quick "ipconfig" in Windows cmd or an "ifconfig" in macOS or Linux concluding can testify you the local IP and mask.
- If you can't subnet, Download this Costless Subnet Figurer tool or go online to a subnet calculator and find your network IP.
Step two
- Download and open Nmap.
- Download Nmap from this official link https://nmap.org/download.html and follow its straightforward installation process.
Step 3
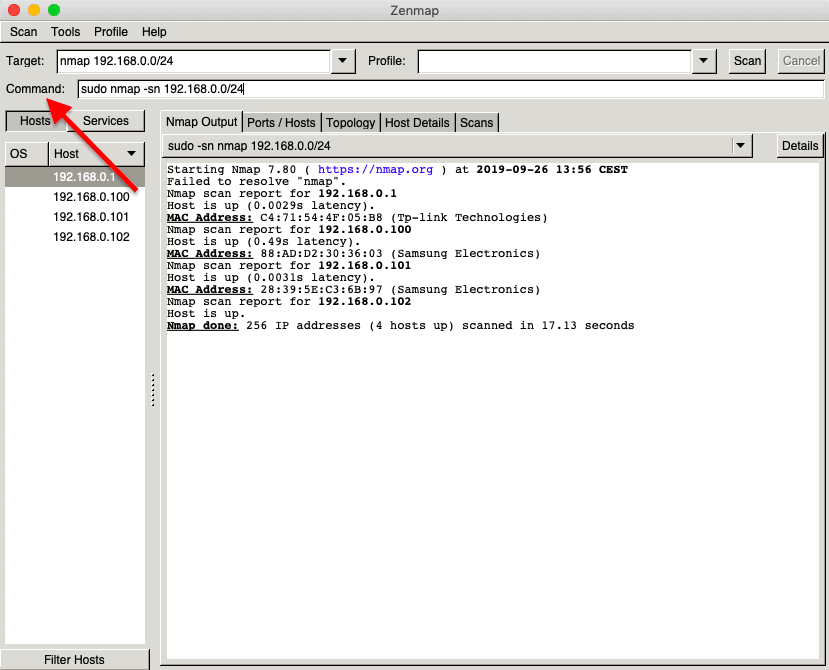
- Open Nmap (or Zenmap) and utilise the control "sudo nmap -sn (network IP)" to scan the entire network (without port scan).
- The control will list machines that respond to the Ping and will include their MAC address along with the vendor.
- Don't forget the "sudo" command.
- Without information technology, you will not come across MAC addresses.
Finding out the device vendor from a MAC address
Ok, so now you were able to find out the IP address using "arp -a" command or through the DHCP Server.
Merely what if you want to know more details about that detail device?
What vendor is it?
Your network segment or LAN might be full of different devices, from computers, firewalls, routers, mobiles, printers, TVs, etc.
And MAC addresses comprise central data for knowing more details about each network device.
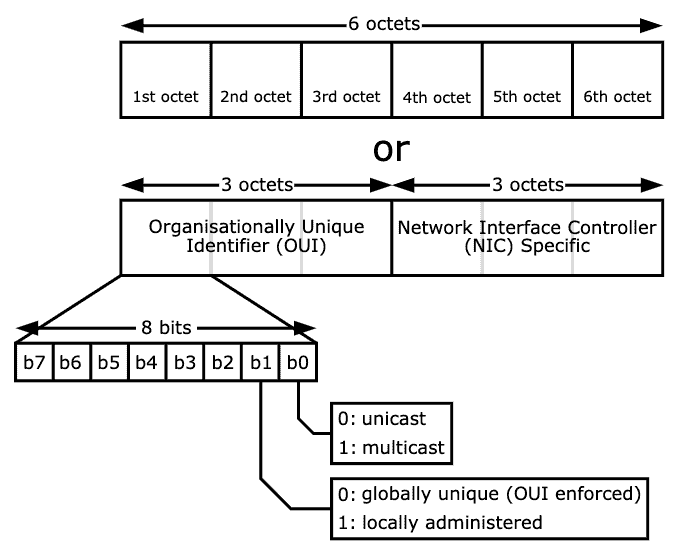
Get-go, it is essential to understand the format of the MAC address.
Traditional MAC addresses are 48 bits represented in 12-digit hexadecimal numbers (or six octets).
The first one-half of the six octets correspond the Organizational Unique Identifier (OUI) and the other half is the Network Interface Controller (NIC) which is unique for every device in the world.
There is not much we tin can do near the NIC, other than communicating with it.
Simply the OUI tin can give usa useful data about the vendor if y'all didn't use Nmap, which tin can also requite yous the hardware vendor.
Using Wireshark OUI Lookup
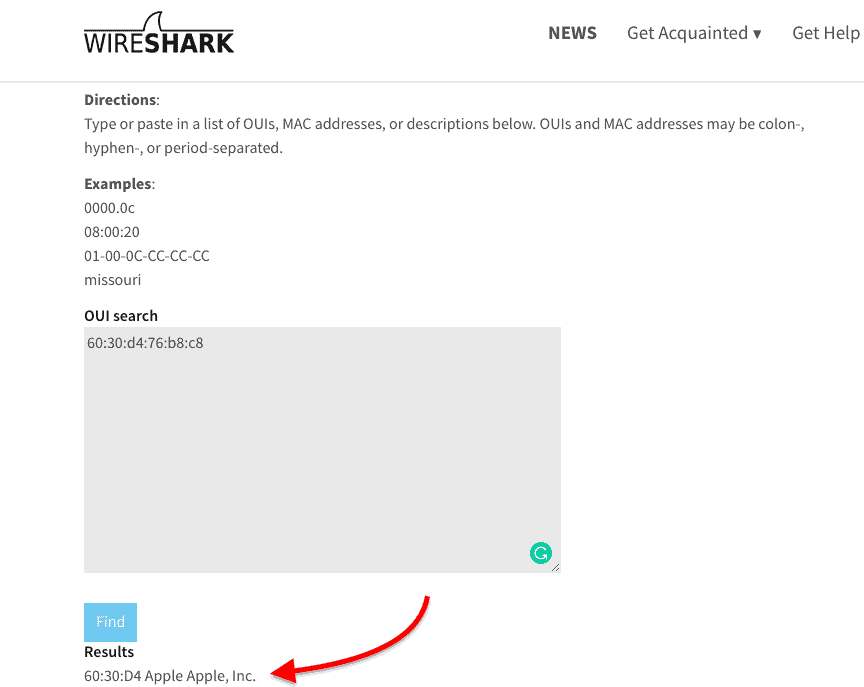
A free online OUI lookup tool like Wireshark OUI Lookup can help you with this.
Just enter the MAC address on the OUI search, and the tool will look at the first three octets and correlate with its manufacturing database.
Using DHCP to view IP info
Although the RARP (the counterpart of ARP) was specifically designed to find IPs from MAC addresses, information technology was apace discontinued because it had many drawbacks.
RARP was quickly replaced by DHCP and BOOTP. Only ARP is still one of the cadre functions of the IP layer in the TCP/IP protocol stack. It finds MAC addresses from known IPs, which is virtually common in today'due south communications. ARP works under the hood to go on a frequently used list of MACs and IPs.
Just you tin also use it to see the current mappings with the command arp -a.
Aside from ARP, yous tin besides use DHCP to view IP information. DHCP Servers are usually in charge of IP assignments. If you lot accept access to the DHCP server, go into the DHCP Client listing and identify the IP with the MAC address. Finally, yous can apply a network sniffer like Nmap, browse your unabridged network, and find IPs, and MACs.
If y'all only want to know the vendor, an online OUI lookup like Wireshark tin can help you find it chop-chop.
Detect a Device or IP Address FAQs
Tin you discover an IP accost from a MAC address?
Yes. Open a Command Prompt window and enter the command arp -a. The output shows all of the IP addresses that are active on your network. The side by side column in the output is headed Concrete Address. This is the MAC accost. Look for the line in the output that has the MAC address that you know and note down the IP accost on that line.
How can I access a device by MAC address?
The easiest way to access a device, knowing the MAC address is to use the arp -a command to notice the related IP address. With this address, you tin can access the device using Remote Desktop Management, a Telnet program, or some other connection facility.
How can I find a device by IP address? (cmd instructions)
You can follow a path to a device if you know its IP address by using the tracert command at the command prompt (cmd). Open a Command Prompt window and type in tracert followed by the IP address that you know. The output will show each router that has a connexion to that device volition pass through.
bardonwearprapart.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.pcwdld.com/find-device-or-ip-address-using-mac-address
0 Response to "What Device Does This Mac Address Belong to"
Post a Comment